Battery charging station for industrial trucks:
Regulations, dangers, alternatives
Regulations, dangers, alternatives
Electrically powered forklifts regularly recharge in a battery charging station to ensure that their batteries always have fresh energy. To ensure safe and fault-free operation, companies must observe numerous safety regulations when planning and integrating battery charging stations.
What are battery charging systems and battery charging stations?
A battery charging system refers to battery charging rooms, battery charging stations, individual charging stations and the electrical devices required for charging.
A battery charging room contains chargers that are physically separated from the batteries during charging. In comparison, batteries and chargers in battery charging stations charge in the same room.
In single charging spaces (charging stations), the battery remains in the vehicle during charging and is not removed.

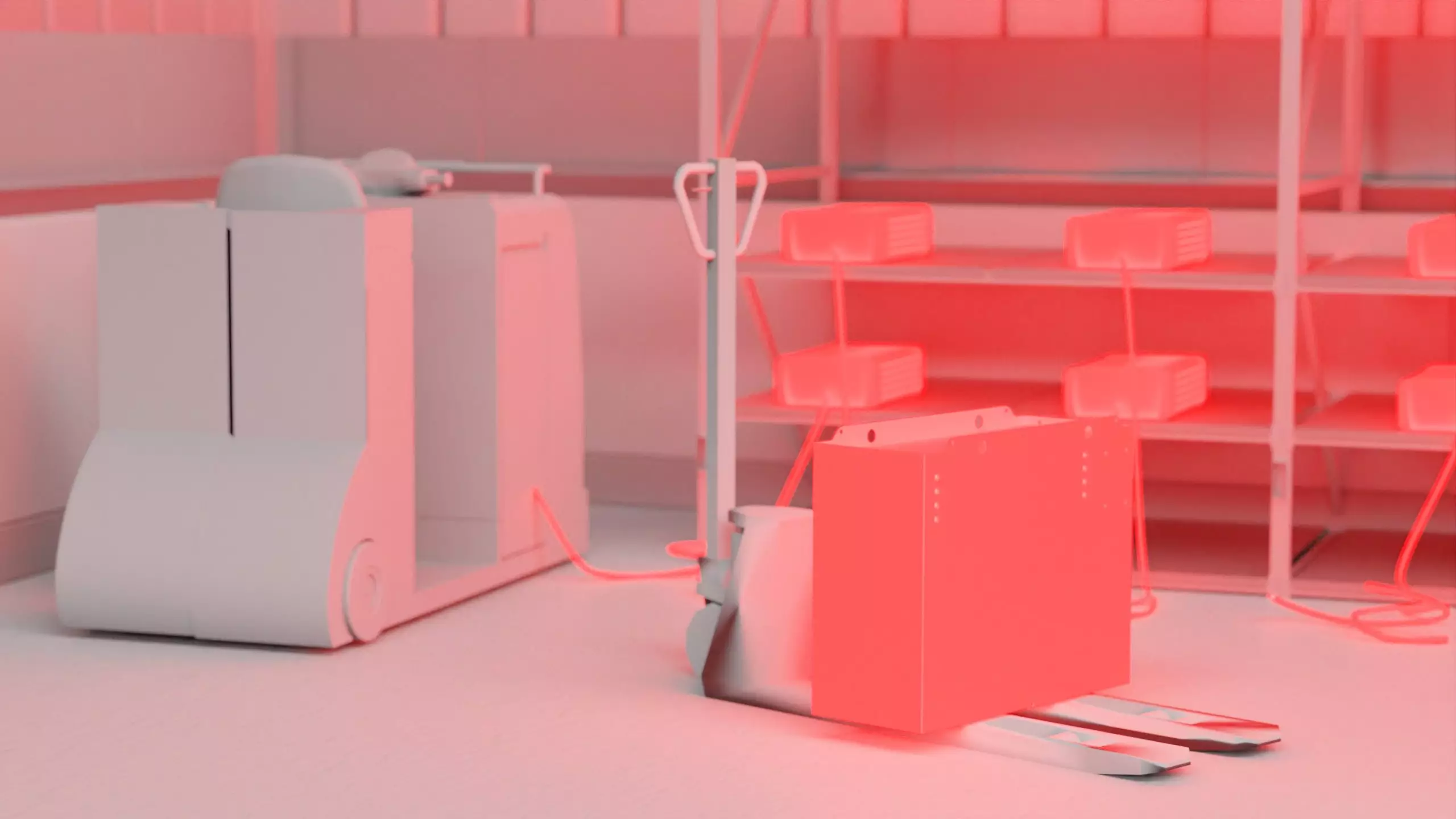
Why do you need a battery charging station?
Battery charging stations are necessary to charge electric powered industrial trucks with lead-acid battery. They must meet certain requirements associated with the handling of lead-acid.
This is because during battery charging, an explosive hydrogen-oxygen mixture is formed that can explode as an oxyhydrogen gas. The lead-acid battery also contains electrolyte liquid of diluted sulfuric acid, which is highly corrosive. Above a certain voltage, touching the battery can cause dangerous body currents.
Battery charging stations should therefore be fireproofed from other areas and need good ventilation. In addition, companies should use warning signs to point out any potential hazards.
Interested in battery charging station?
Contact us!
Contact us!
What are the regulations for the battery charging station?
In Germany, the DIN VDE 0100 series of standards applies to the construction of low-voltage installations. The standard regulates how the planning, construction and testing of low-voltage installations are to be implemented in order to ensure a high standard of safety. It specifies conditions for safe working in and around electrical installations such as battery charging stations.
This also applies to battery charging stations, which are classified as “electrical operating facilities” or “closed electrical operating facilities” according to DIN VDE 0100. To prevent hazards to personnel, companies must secure battery charging stations against electric shocks, thermal effects and interference voltages as well as electromagnetic interference factors.
The standard provides companies with specifications for work, operation and maintenance procedures. It also explains the procedure for maintenance work on cables in or near the charging station and which activities are permitted in the battery charging station.
The aim is to avoid hazards to persons and to achieve a particularly high level of operational safety. This means that both personal and system protection are always important during installation and subsequent measures for modifications.
During its service life, the battery charging station is regularly maintained, inspected and repaired in the event of any defects.
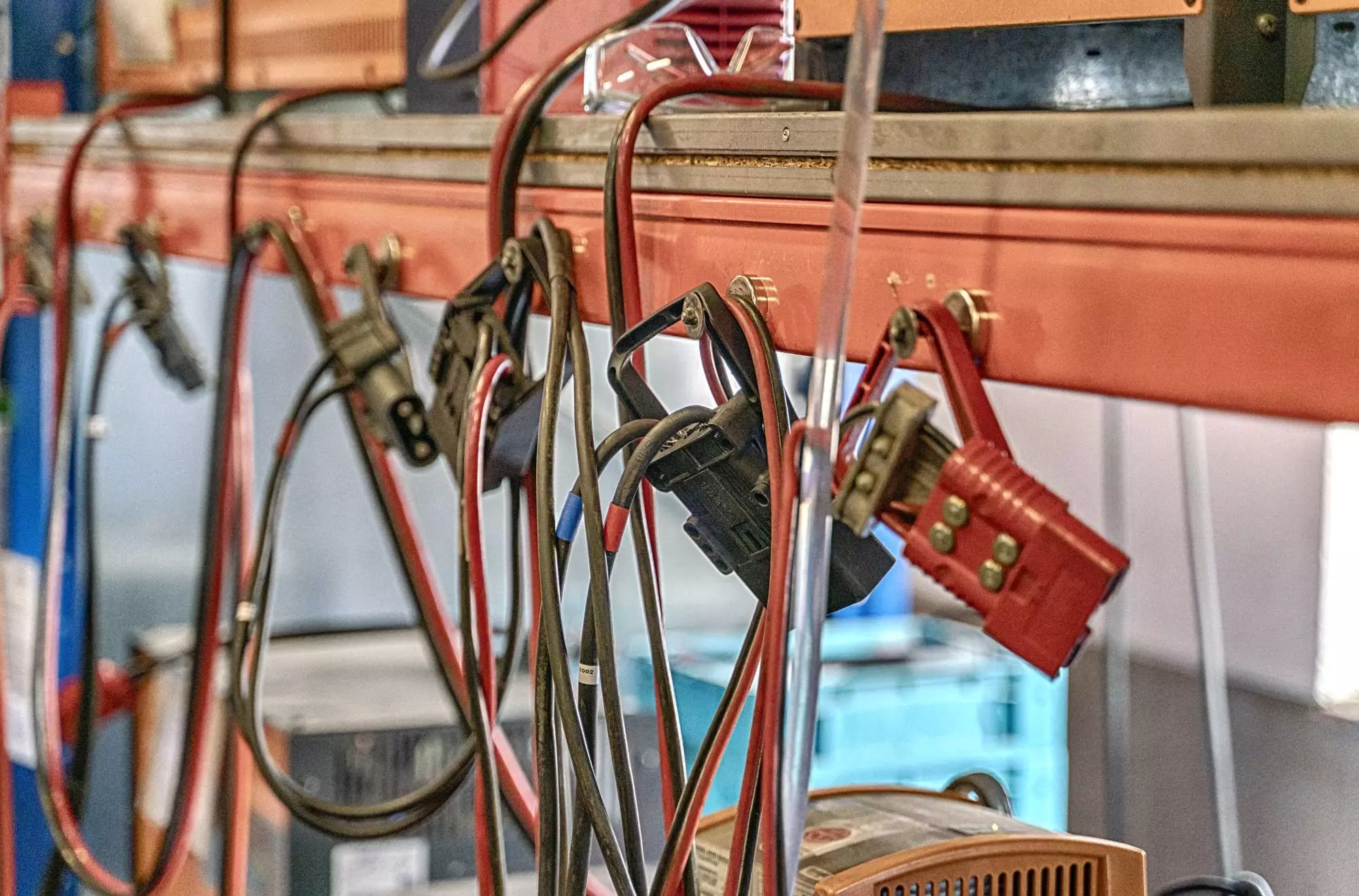


What are the spatial requirements for a battery charging station?
A single charging station is at least 2 meters high. If a forklift is in the charging station, the operating sides must be freely accessible with an aisle width of at least 0.6 meters.
The following spatial requirements exist:
- do not set up in enclosed large garages
- not subject to fire, explosion or explosive hazards
- neither damp nor wet
- allow for possible flooding or groundwater rise
- frost-free, cool place without direct sunlight
Permanent markings, walls, obstructions, or clearances to separate from other operating areas (from a rated voltage of more than 60 volts and a rated charging power of more than 1 kW)
A crack-free and antistatic floor with a grounding resistance of 108 Ω or less is a requirement. Companies should secure the ceiling, walls and floor of the battery charging station to be electrolyte resistant.
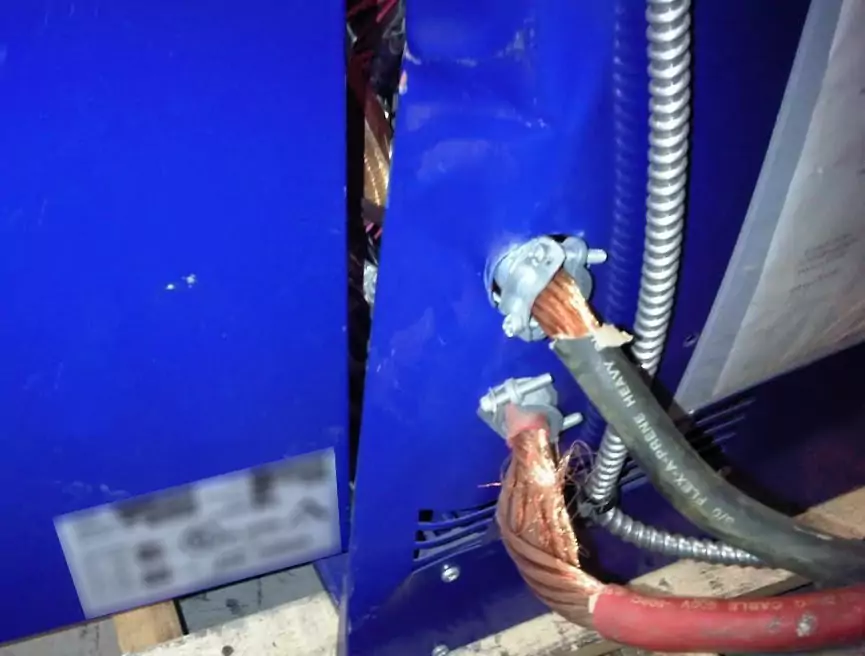
For safe use, it is important to protect the charging cables of the battery charging station from damage by being run over, crushed or sheared off.
Fire regulations
To prevent battery charging stations from catching fire, companies must separate and secure them in a fire-retardant manner from other areas such as warehouses or production facilities (minimum fire resistance class F30). The required fire resistance time for building components is 30 minutes.
Other fire protection specifications include:
- Integrate fire extinguishers and fire alarm systems
- Keep a distance of at least 2.5 meters to combustible building materials or materials
- Do not use mobile equipment in the charging area
- safety zone of half a meter without flying sparks, glowing bodies, electric arcs or open flames
- absolute ban on smoking
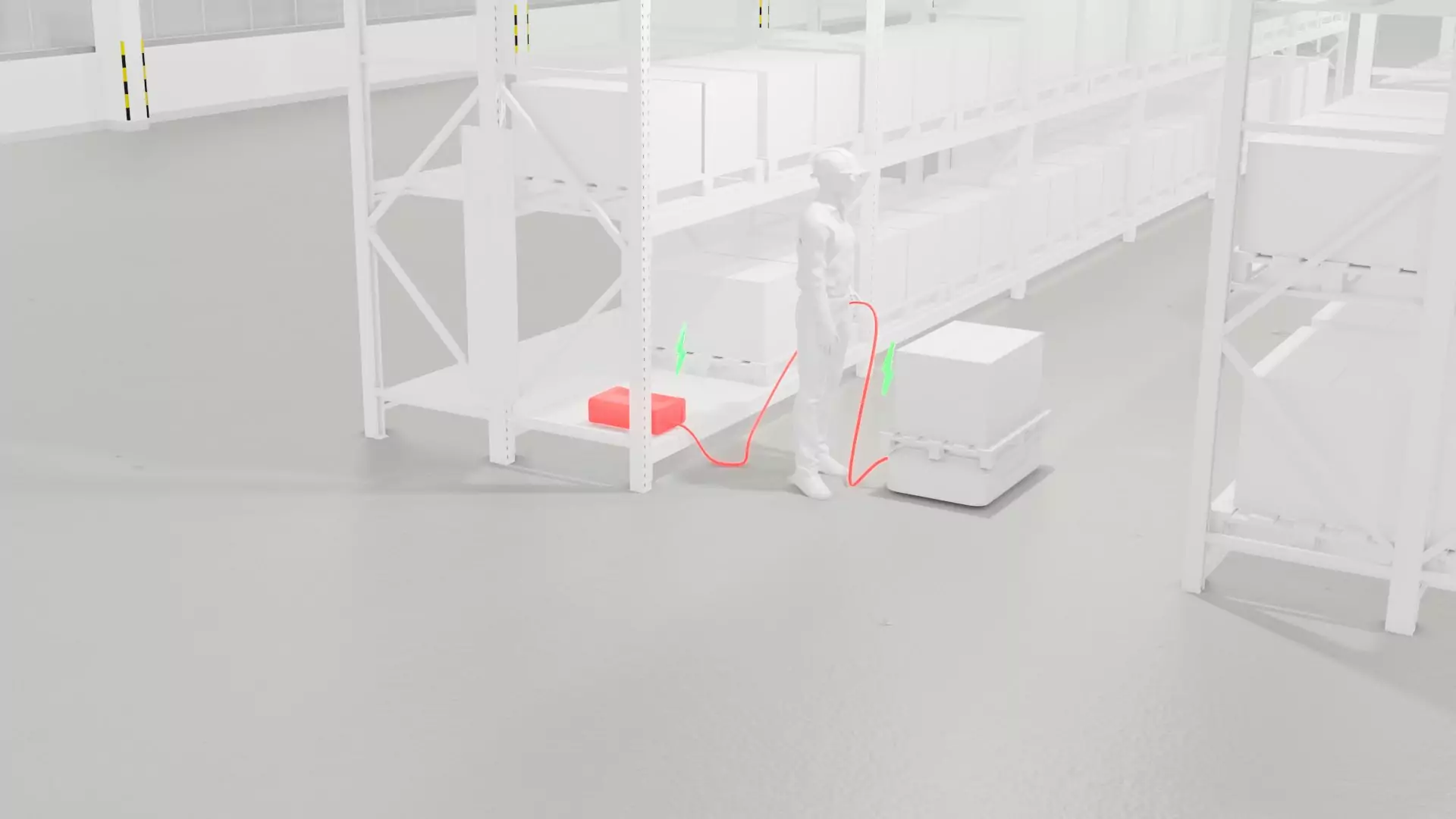

Battery charging station ventilation
Permanent ventilation through technical or natural ventilation slots is a prerequisite for the safest possible use. Ventilation is sufficient if the air is exchanged at least 2.5 times every hour.
After the charging process, the ventilation should still be active for at least one hour so that the entire hydrogen mixture is transported outside.
If the supply and exhaust air are on the same wall, there must be at least two meters between them so that they do not draw in dangerous gases and vapors. Fresh air ventilation is located near the floor, and exhaust ventilation is located above the battery level.
Employees regularly inspect and clean the pipes and ducts.
Engineered ventilation requires a mutual interlock or alarm between the charger and the ventilation system if the necessary airflow for the charging process is not provided.
For natural ventilation, the air velocity should be at least 0.1 meters per second. Windows and doors are considered to be free wall openings only if they are open continuously throughout the charging process.
If several batteries are charging simultaneously in one room, the total air volume flow for the battery charging station is calculated from the sum of the air volume flows of all batteries to be charged in the area.
Marking of battery charging stations
To ensure that battery charging stations are used as safely as possible, companies can make use of a few tricks. For example, warning signs inform employees of potential hazards from overcharging, fire, naked lights and the absolute ban on smoking.
Each station has an emergency shower, a sink, an eyewash station and a first-aid kit. In the event of an accident, employees have the opportunity to administer first aid directly on site.
A water connection with a hose in the battery charging station is useful for cleaning the single-charge compartment and the battery.


Use of battery charging stations – dangers
Several hazards are associated with the use of battery charging stations. Companies should be aware of the following when dealing with battery charging stations:
- Hydrogen floats on the battery surface because it is lighter than oxygen. Therefore, when the battery compartment is opened, there is a risk that employees will inhale the hydrogen in a strong concentration.
- During charging, the battery feeds itself with high charging currents – this significantly shortens the service life. If the battery is overcharged, the temperature increases, creating an acute fire hazard.
- If the battery is overcharged, an explosive oxygen-hydrogen mixture develops, which can explode as oxyhydrogen gas. The critical charging voltage is more than 2.40 volts per cell, above which the hydrogen outgassing reaches a dangerous concentration. Then there is an acute danger of explosion.
- When replacing batteries and during maintenance, employees come into contact with hazardous chemicals such as electrolytes. This can cause accidents in the workplace.
- Forklifts mainly charge after employees’ shifts end to minimize disruption to general production. Unattended operation increases hazards.
- When employees want to connect forklifts to the charger, there is a risk that they will confuse the electrical polarity of the connection points. Even if terminals or connectors are not tight, fires or further damage can occur.
Disadvantages of using battery charging rooms
Charging lead-acid batteries in battery charging stations requires a great deal of maintenance. In addition, battery removal and installation is very time-consuming and unpopular for employees. Battery charging stations also pose a significant risk in terms of occupational safety.
For example, employees must regularly check the traction batteries for electrolyte density or top up with water. When doing so, they wear neat, acid-proof protective clothing including goggles, gloves, aprons and shoes to prevent injuries.
Individual charging stations and batteries must always be in a clean condition. If the components become dirty, leakage current can build up. This results in an increased risk of fire and injury.
For environmental reasons, no electrolyte solution may enter the public sewage system or sewage treatment plants. If electrolyte-containing liquid should leak out, it is mopped up with an absorbent, neutral binder. Employees then collect the electrolyte for neutralization in acid- and alkali-resistant containers.
Since forklifts usually charge unattended, battery charging stations require RCDs residual current devices with a differential rated current of ≤ 300 mA.
If this is not possible, the operator must provide protection against overload or short circuit on the mains side. On the charging side, there is an overcurrent protection device that adapts to the largest charging current.
Automated charging stations: Inductive energy transmission as an alternative for more safety
Due to the versatile disadvantages of the lead-acid battery, more and more companies are turning to modern lithium-ion batteries.
A permanently integrated battery charging station is no longer necessary for charging the lithium-ion battery. In contrast to charging with lead-acid batteries, companies do not have to install a ventilation system for the use of lithium-ion batteries. Energy transfer is hydrogen-free. No hazardous gases are formed. This increases employee protection while reducing installation costs.
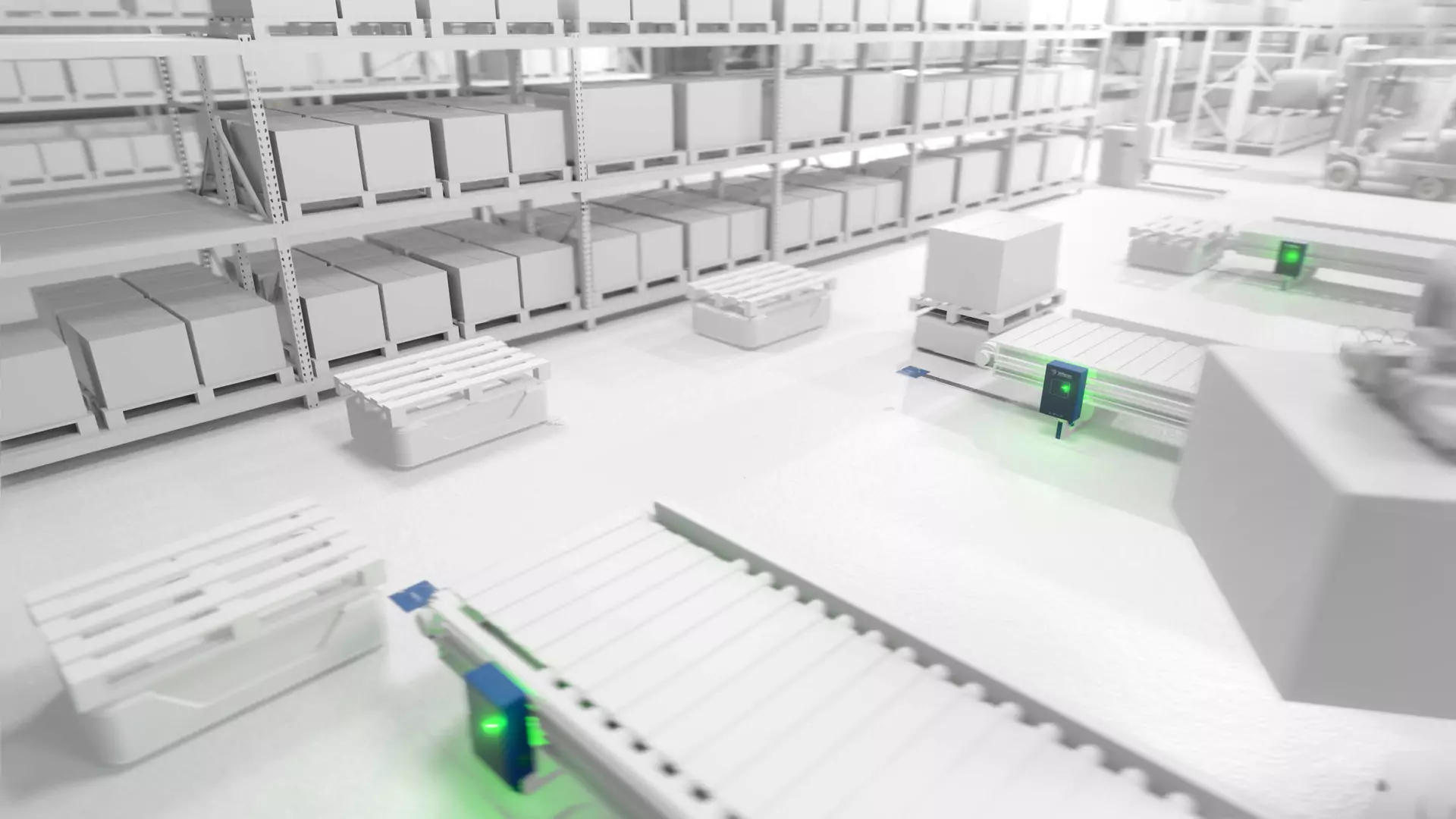

Automated charging and no deep discharge
In addition, lithium-ion batteries do not require deep discharge and are characterized by their fast charging capability. This allows them to be charged temporarily.
In conventional battery charging stations, the batteries are charged with a plug. The process interrupts employees in their daily workflow. Instead of taking care of their transportation tasks, they also have to worry about charging the battery. In the day-to-day doing, this task often falls by the wayside. Those who only stop for a few minutes usually do not connect the vehicle to the desired charging station. As a result, the vehicle batteries are empty at the end of the shift and have to be charged for several hours before the vehicle is ready for use again.
Inductive charging systems, on the other hand, enable an automated charging process that kicks in as soon as the vehicle is parked or stops. Even during short stops, the battery is efficiently supplied with energy. Employees do not have to act manually during the charging process and are thus relieved of charging tasks. The vehicles always have sufficient energy. This eliminates downtimes and increases vehicle availability by up to 32%.












